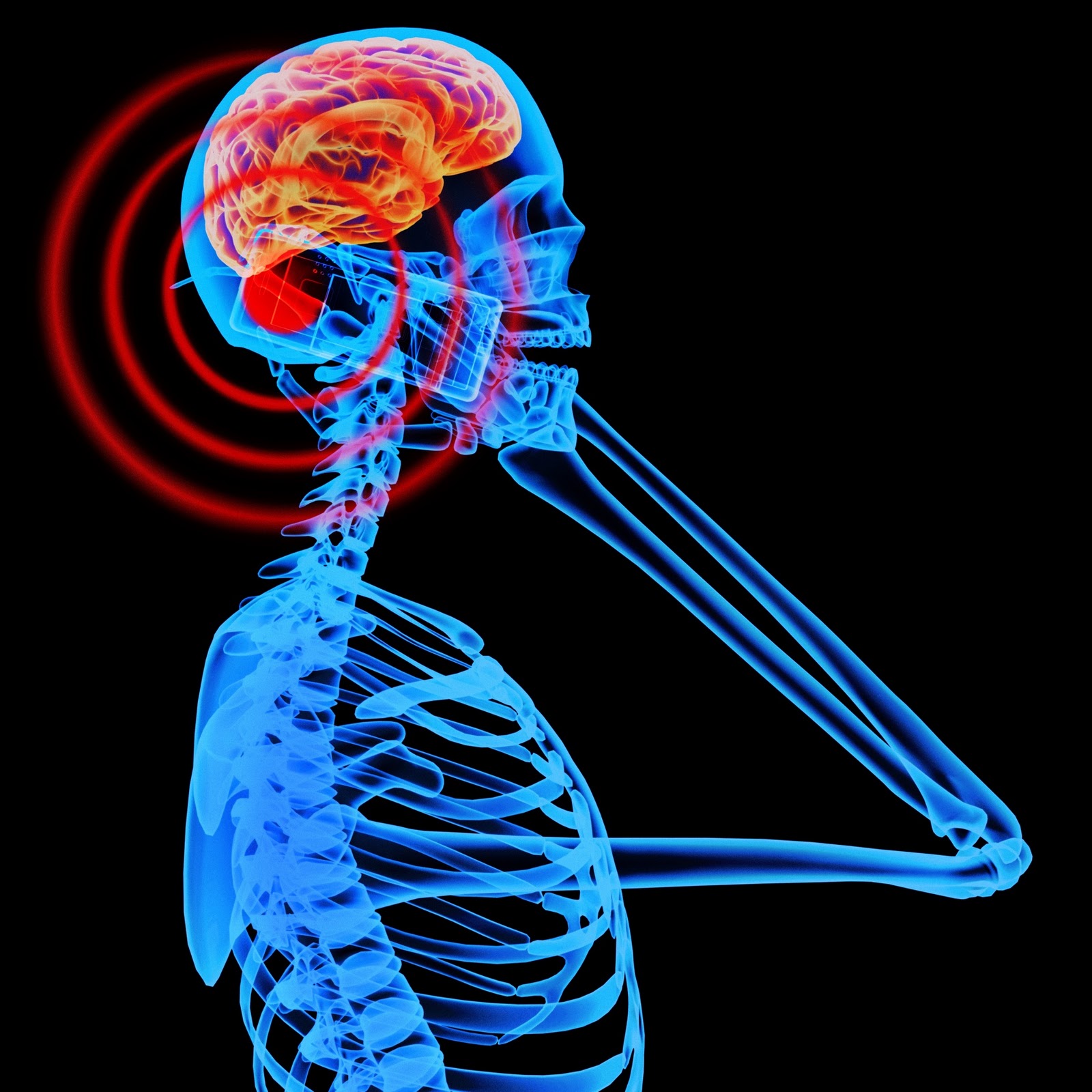
THE World Health Organisation (WHO) and the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) have allayed the fear of Nigerians over the alleged health-related hazards emanating from the siting of Base Transceiver Stations (BTS) near residential areas and the use of mobile phones .
At the first West African Conference on Electromagnetic Fields (EMF) Exposure and Health with the theme “Harmonizing EMF Policy, Exposure Limits and RIsk Communication in West AFrica“, organised by the Ministry of Communications Technology, NCC and ECOWAS, yesterday in Lagos, WHO’s Director, Dr. Emilie van Deventer disclosed that the global health body had spent a lot of money in the last 15 years on research but yet to get a confirmed and concrete evidence on dangers of EMF from mobile phones and BTS..
Deventer said : “Today research does not suggest any concrete evidence of adverse health effect from exposure to radio frequency field at levels below those that cause tissue heating.
“Research has not been able also to provide support for a causal relationship between exposure to EMF and self- reported system.”
She explained that governments must come up with clear roles and responsibilities, adding that there was need for Nigeria to adopt and comply with international standards.
According to the Minister of Health, Prof. C.O Onyebuchi, research findings have been mixed. While some people documented a possible association between living close to high tension cables and cancer of the blood and leukemia in children, others say there is no association because there is limited evidence to support that.
Why is there concern that cell phones may cause cancer or other health problems?
There are three main reasons why people are concerned that cell phones (also known as “mobile” or “wireless” telephones) might have the potential to cause certain types of cancer or other health problems:
- Cell phones emit radiofrequency energy (radio waves), a form of non-ionizing radiation, from their antennas. Tissues nearest to the antenna can absorb this energy.
- The number of cell phone users has increased rapidly. As of December 2014, there were more than 327.5 million cell phone subscribers in the United States, according to the Cellular Telecommunications and Internet Association. This is a nearly threefold increase from the 110 million users in 2000. Globally, the number of subscriptions is estimated by the International Telecommunications Union to be 5 billion.
- Over time, the number of cell phone calls per day, the length of each call, and the amount of time people use cell phones have increased. Cell phone technology has also undergone substantial changes.
What is radio-frequency energy and how does it affect the body?
Radio-frequency energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation can be categorized into two types: ionizing (e.g., x-rays, radon, and cosmic rays) and non-ionizing (e.g., radio-frequency and extremely low frequency, or power frequency). Electromagnetic radiation is defined according to its wavelength and frequency, which is the number of cycles of a wave that pass a reference point per second. Electromagnetic frequencies are described in units called hertz (Hz).
The energy of electromagnetic radiation is determined by its frequency; ionizing radiation is high frequency, and therefore high energy, whereas non-ionizing radiation is low frequency, and therefore low energy.
The frequency of radio-frequency electromagnetic radiation ranges from 30 kilohertz (30 kHz, or 30,000 Hz) to 300 gigahertz (300 GHz, or 300 billion Hz). Electromagnetic fields in the radiofrequency range are used for telecommunications applications, including cell phones, televisions, and radio transmissions. The human body absorbs energy from devices that emit radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. The dose of the absorbed energy is estimated using a measure called the specific absorption rate (SAR), which is expressed in watts per kilogram of body weight.
Exposure to ionizing radiation, such as from x-rays, is known to increase the risk of cancer. However, although many studies have examined the potential health effects of non-ionizing radiation from radar, microwave ovens, cell phones, and other sources, there is currently no consistent evidence that non-ionizing radiation increases cancer risk (1).
The only consistently recognized biological effect of radio-frequency energy is heating. The ability of microwave ovens to heat food is one example of this effect of radio-frequency energy. Radio-frequency exposure from cell phone use does cause heating to the area of the body where a cell phone or other device is held (ear, head, etc.). However, it is not sufficient to measurably increase body temperature, and there are no other clearly established effects on the body from radio-frequency energy.
It has been suggested that radio-frequency energy might affect glucose metabolism, but two small studies that examined brain glucose metabolism after use of a cell phone showed inconsistent results. Whereas one study showed increased glucose metabolism in the region of the brain close to the antenna compared with tissues on the opposite side of the brain (2), the other study (3) found reduced glucose metabolism on the side of the brain where the phone was used.
Another study investigated whether exposure to the radio-frequency energy from cell phones affects the flow of blood in the brain and found no evidence of such an effect (4).
The authors of these studies noted that the results are preliminary and that possible health outcomes from changes in glucose metabolism are still unknown. Such inconsistent findings are not uncommon in experimental studies of the biological effects of radio-frequency electromagnetic radiation (5). Some contributing factors include assumptions used to estimate doses, failure to consider temperature effects, and lack of blinding of investigators to exposure status.